Click here to comment on YouTube
The circulatory system, like every other system in the body, is very important. Doctors address health-related blood pressure and heart issues by prescribing various medications.
Let’s take a look at five kinds of cardiovascular drugs and how they work.
Topic Outline
Types of Cardiovascular Drugs:
Anticoagulant Drugs
Anticoagulant drugs help to decrease clotting.
Excessive clotting can block blood vessels, cut off oxygen and nutrient delivery to different tissues, and can even lead to a stroke.
These types of cardiovascular drugs prevent the formation of new clots.

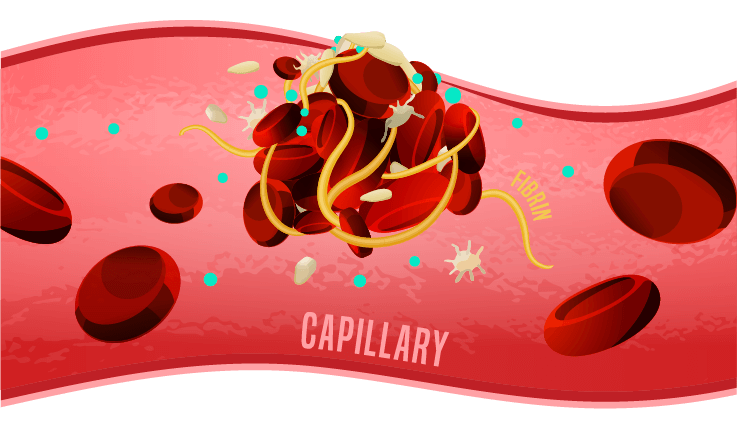
An example of an anticoagulant is heparin. This binds to a specific enzyme called antithrombin III which results in the reduction of the formation of blood clots.
In my previous video on hemostasis where I covered the blood clotting process, I showed how one of the steps in the clotting process is the formation of thrombin.
We found that thrombin converts fibrinogen (which is soluble and active) into fibrin that forms a fibrin mesh holding everything together to form the clot.
As heparin binds to antithrombin III, thrombin becomes inactive. If thrombin is inactive, it will no longer stimulate the production of fibrin, and that will reduce the chances of forming the clot.
If any of that doesn’t make sense, make sure to check out my video on hemostasis where I go into that in more detail.
ACE Inhibitors
These are cardiovascular drugs that block the angiotensin-converting enzyme. This enzyme is a very important enzyme that plays a role in converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
Angiotensin II is a very potent vasoconstrictor which causes your blood vessels to constrict resulting in increased blood pressure.
As you would imagine, if a person has high blood pressure, you want to do what you can to reduce blood pressure.
To address this, ACE inhibitors block angiotensin-converting enzymes from producing angiotensin II. This in turn will reduce vasoconstriction causing a decrease in blood pressure.
Beta-Blockers
These are cardiovascular drugs that have the effect of decreasing heart rate and force of contraction. This causes your blood pressure to go down and slows down the heart rate.
Patients with cardiac arrhythmia can benefit from the effects of beta-blockers. They help to prevent heart attack, or in some cases, to help lower blood pressure.
Let’s see how this works.
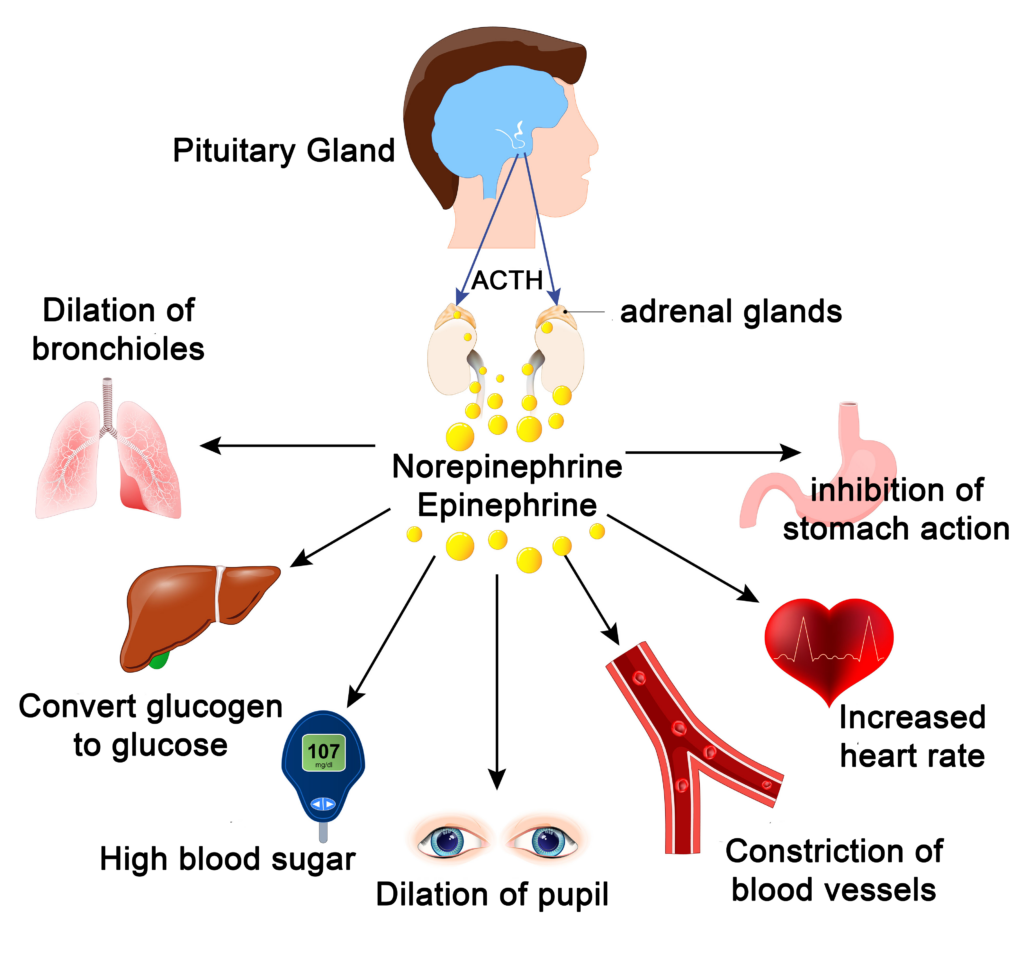
Let’s say, you get excited, or you’re exercising and your heart rate increases. Your sympathetic nervous system causes an increased heart rate with the release of the hormone epinephrine or adrenaline.
This hormone binds to specific receptors (beta receptors) in the heart muscle, arteries, kidneys, and other places leading to stress responses which include an increased heart rate and blood pressure.
A beta-blocker does exactly what it sounds like it will do. It’s what we call a competitive antagonist.
It blocks the receptor sites on the beta receptors. As a result, epinephrine cannot bind to them and so, it won’t be able to do what it does.
This can help to reduce heart rate and blood pressure basically leading to the opposite of the fight or flight response.
With a person that has high blood pressure and some other heart-related issues, this may be beneficial.
Calcium Channel Blocker
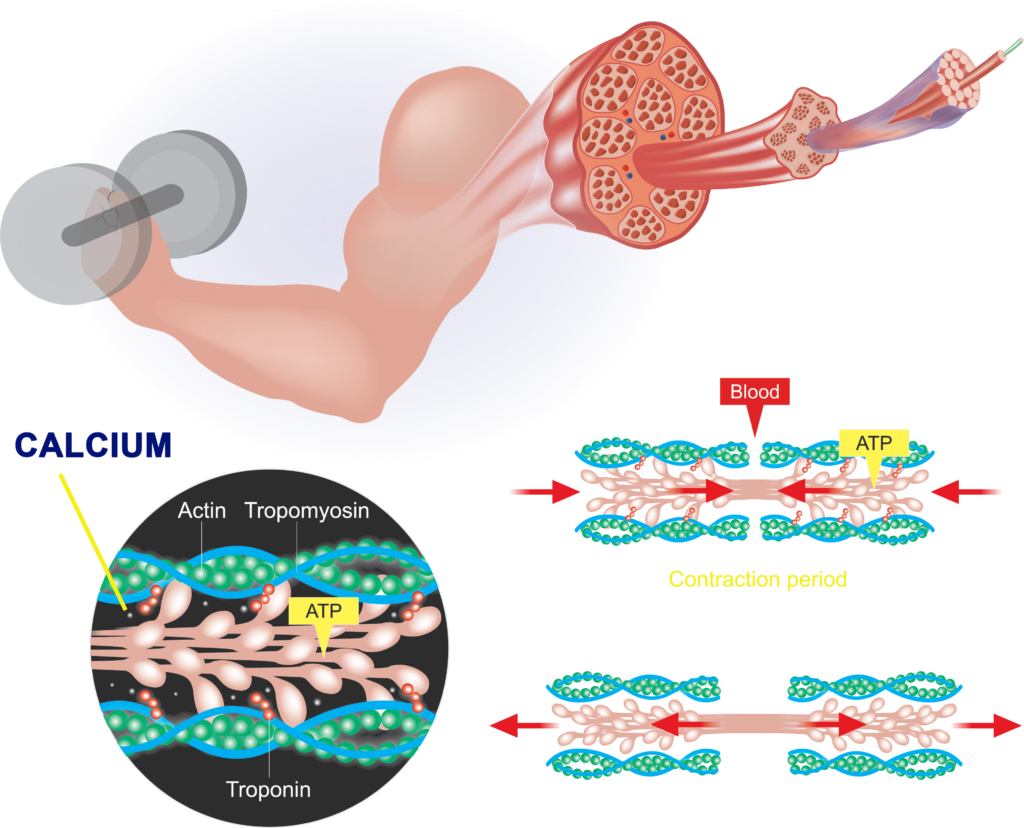
The calcium stored inside the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle cells is a very important ion when it comes to muscle contraction.
As muscles are stimulated, these ions are released through calcium channels and enter the cytoplasm of the cell. This step is a crucial step that causes muscle contraction.
As you can imagine, calcium channel blockers will block those calcium channels, preventing calcium from entering the muscle cells.
By doing that, it reduces contraction, which may help with things like lowering blood pressure and other related problems with the heart.
It’s like a hose. If you squeeze the hose, you increase the pressure. We’re trying to reduce the squeezing to reduce the pressure.
Diuretics
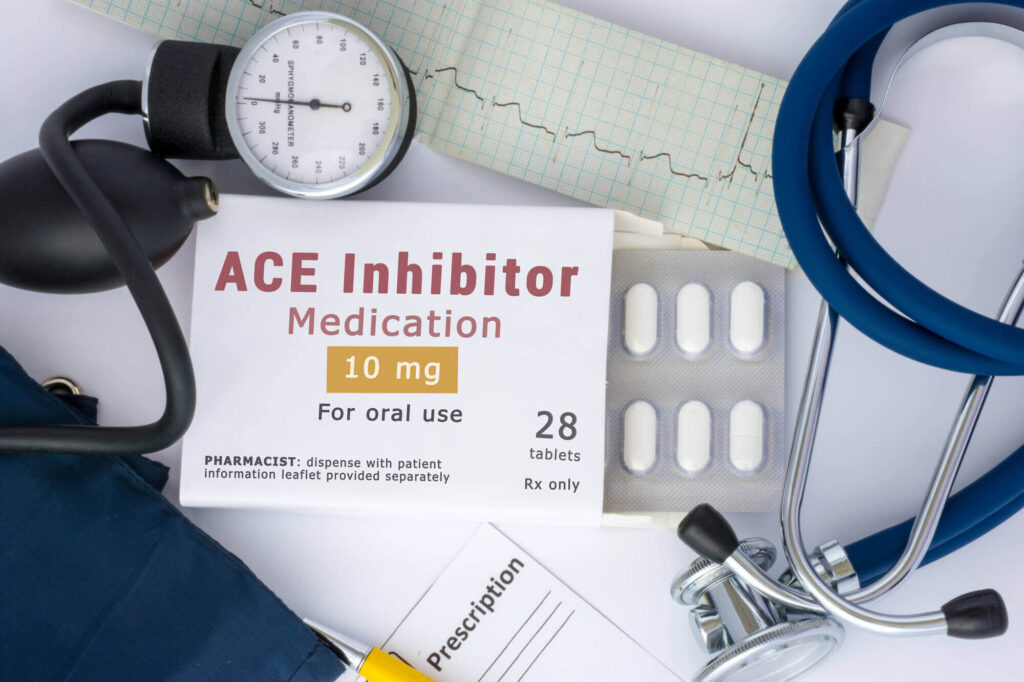
Diuretics decrease blood pressure in a different way. To understand how these drugs work, we have to know a little about the kidney.
Nephrons are the functional unit of the kidney. A number of processes take place in the nephron to filter the blood.
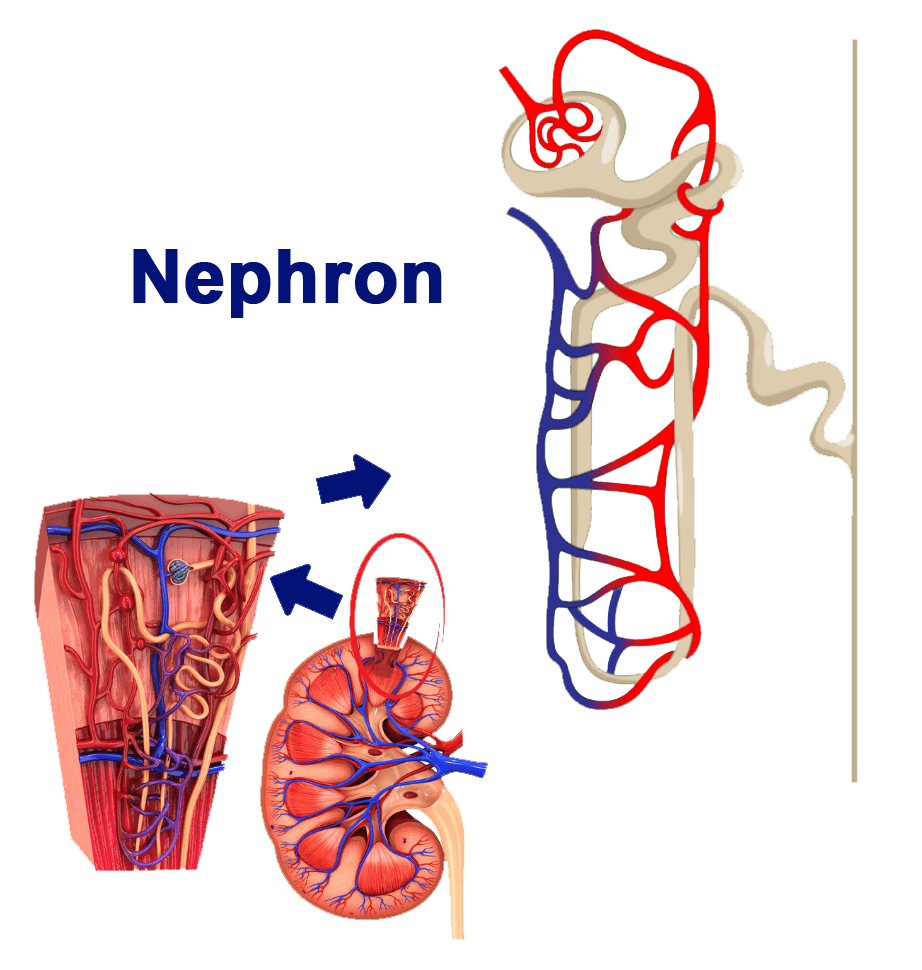
At a certain point, one of the events that happen is sodium reabsorption where the kidneys absorb back some sodium after the blood is filtered. This also causes water to come along with it.
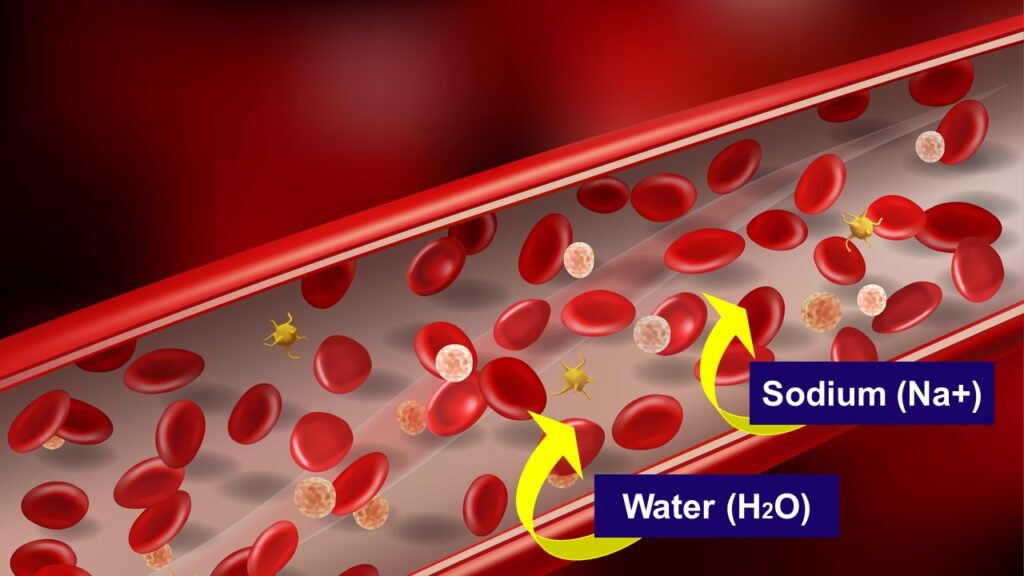
Diuretics work by decreasing sodium reabsorption causing the kidneys to get rid of sodium. And by doing that, there will be less water reabsorption.
And yes, the body gets rid of more water and you pee a lot more. Hence, they are called “diuretics.”
As you excrete more fluid, you’re also decreasing the amount of fluid in the blood. The lesser the amount of fluid going through the blood vessels, the lesser is the pressure in the blood vessels.
That’s what we want in cases of high blood pressure.
Conclusion
I tried to touch on the major points to help explain the general mechanisms behind how these drugs affect the cardiovascular system. But, there is a lot more to them that I can’t cover in a short episode.
Obviously, there are other systems that these drugs can affect. There are also many other drugs that affect the cardiovascular system. But, here’s the cool part. We have comments.
If you know of a different drug and its mechanism, go ahead and share it in the comments below, so that we can all continue learning.