Mendel’s pea plant experiment which lasted for over a decade was a huge scientific breakthrough.
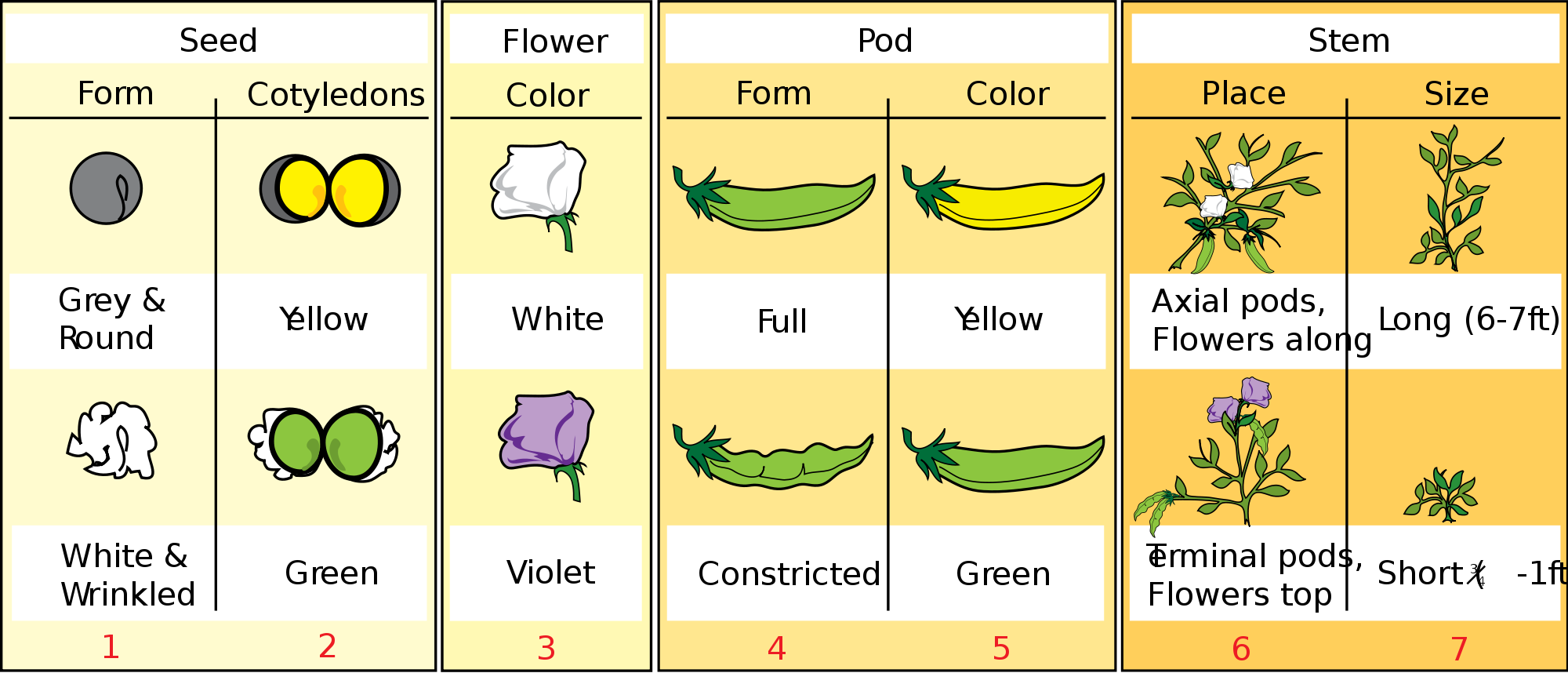
The pea plant has Seven different variable traits. Scientists say that it was due to his luck and the ever important selection of the plant that Mendel succeeded. They are:
- Flower color is purple or white;
- Seed color is yellow or green;
- Flower position is axial or terminal;
- Pod shape is inflated or constricted;
- Stem length is long or short;
- Pod color is yellow or green; and
- Seed shape is round or wrinkled.
So, if we cross bred any pea plants, there can be hundreds of permutations and combinations possible. So, what Mendel did was select one trait at a time. For example: pea albumin color, which can either be yellow or green.
He just wanted to find out whether crossbreeding a pea plant with all other traits except the seed colour the same, would yield a half green and half yellow pea, which would be amazing as well as weird.
However, he found out that the seed color of daughter plants or offspring plants was yellow, which confused him greatly. So, he tried the same thing again and again, this time selecting and crossbreeding plants while focusing on just one trait and found out that either one of the trait was expressed on the combination of two variable features of a same trait.
On basis of this, he proposed the Law of Dominance.
The next two laws were based on further study of this exquisite phenomenon. They are the Law of Segregation and Law of Inheritance.
Definition of Terms
Now before we start understanding the ever-so-important laws, let’s deal with a little more vocabulary first!
Genotype
These are genes present in an organism. Example: for tall trait, they are TT; for short, they are tt.
TT and tt is homozygous which means pure breed. If you breed TT with a TT, you will get a pure breed TT .The same goes for tt.
Tt is heterozygous which means hybrid.
Phenotype
Phenotype is how the trait physically shows up in the plant or a living being in general. The simplest way to determine an organism’s phenotype ? Look at it. Examples of phenotypes: blue eyes, brown fur, striped fruit, yellow flowers, small flowers,etc.
Allele
Allele is a singular t from tt. Even in Tt, t singularly is known as an allele and T is also another allele. Alleles are little codes, for example ACTGC in DNA means red or say, yellow fruit.
The two of them together are needed to successfully express a trait in an organism. However, they are separated during meiosis.
How their separation affects the phenotypic character of an organism, we shall see in detail in the next post, as well as about the Law of Dominance, and phenotypic and genotypic ratios.

i love for biology and i like for jone mendal but thise expriment was very vell in pea plant risarch
Srushti
Excellent! Especially how accurately you explained basic vocabulary without the usual ramblings. Looking forward to future posts.
Learned far too late in life my interest in Biology especially genetics.
Thank You,
Donna
Hey Srushtik
Thanks a lot for posting this content 🙂
you’ve really helped me a lot in understanding
the Concept of Dominance and helped me out with the question
that WHY DID MENDEL EXPERIMENTED WITH PEA PLANTS
Well, if you have some more knowledge about this questions please do share it with me and others who follow your posts.
Looking forward for your future posts.
Thank You,
Deipika 😉