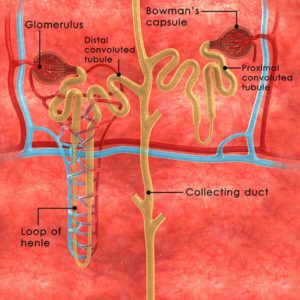
As we have learned from my previous article on nephrons, the renal tubule is the part of the nephron in which the filtrate from the glomerulus enter. It consists of the following:
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle divided into the:
- Distal convoluted tubule
- The collecting ducts
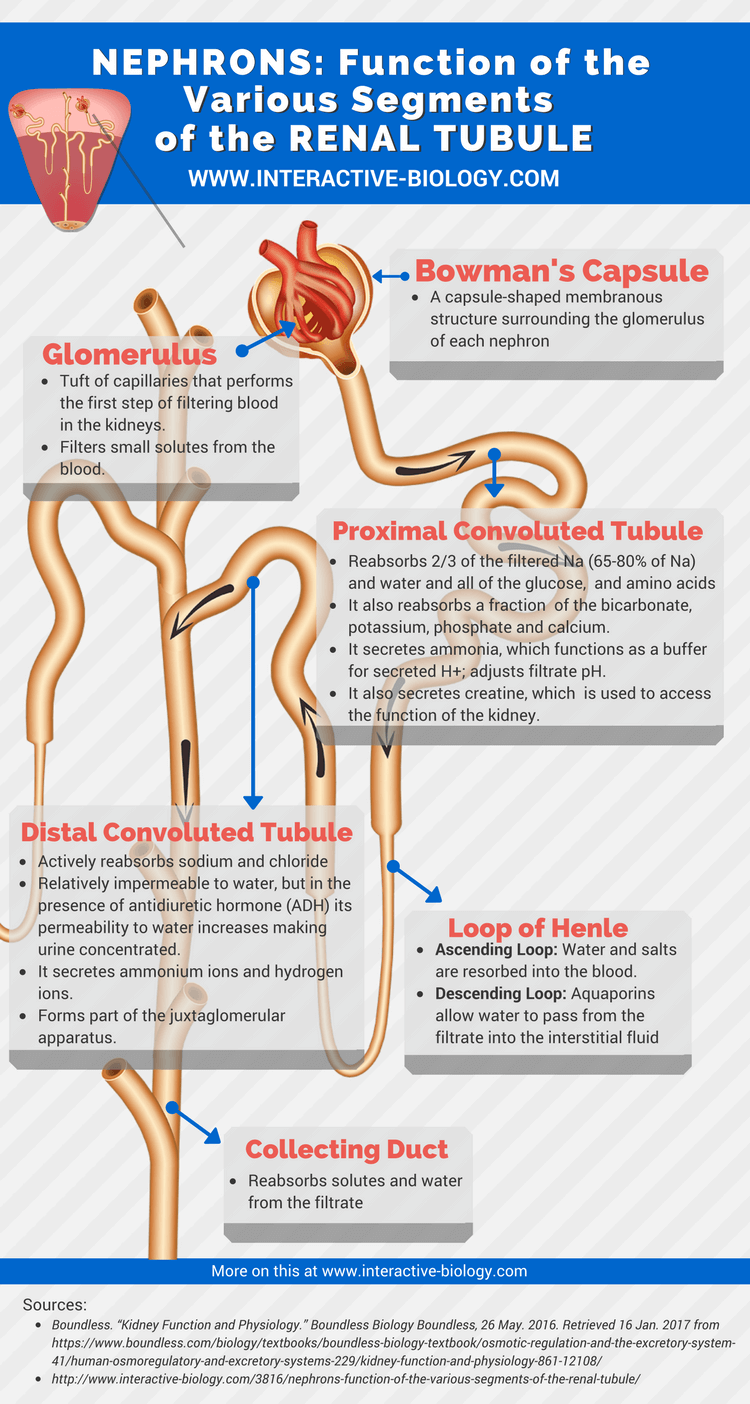
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
This is the first part of the renal tubule and it lies in the cortex of the kidney, close to the renal corpuscle. Fluid that is filtered from the Bowman’s Capsule enters into the proximal tubule. It contains brush border, and is made up of cubiodal epithelium. It has an acidophilic cytoplasm due to the number of mitochondria.
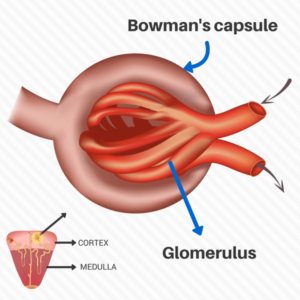
Functions of PCT
- PCT reabsorbs 2/3 of the filtered Na or (65-80% of Na) and H2O
- It reabsorbs all of the glucose, and amino acids
- glucose is reabsorbed via Na-Glu cotransporter
- It also reabsorbs a fraction of the bicarbonate, potassium, phosphate and calcium
- It secretes ammonia, which functions as a buffer for secreted H+. It also secretes creatine, which is used to access the function of the kidney.
Loop of Henle
After filtrates leave the PCT, it enters the Loop of Henle. This is a u-shaped structure tube and it contains different segments which perform different functions.
Thin Descending Loop (TDL)
- reabsorbs water(H2O) passively
- it is impermeable to sodium(Na)
- it allows the urine to be concentrated, the urine in the TDL is hypertonic
Thick Ascending Loop
- In this part of the loop, Na, K and Cl is actively reabsorbed
- It is impermeable to H2O
- this segment makes the urine less concentrated
The Loop of Henle reabsorbs 10-20% sodium and chloride and 10% of the filtered water.
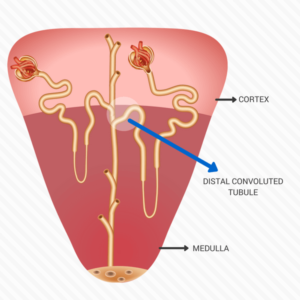
Distal Convoluted Tubule
- this segment of the renal tubule is lined with simple cuboidal epithelium and has no brush border
- is actively reabsorbs sodium and chloride
- it is relatively impermeable to water, but in the present of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) its permeability to water increases making urine concentrated.
- it secretes ammonium ions and hydrogen ions.
- forms part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus
The Collecting Ducts
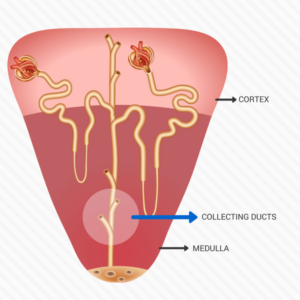
The CD runs through the cortex into the medulla and opens into the renal papilla. Its epithelium varies from cuboidal to columnar epithelium(near the papilla). It is the final segment of the renal tubule. It has two types of cells:
1. Principal cells
- Reabsorbs sodium and water
- Secretes potassium
These functions are regulated by ADH and aldosterone. Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption and increases potassium secretion. ADH on the other hand enhances water reabsorption. Therefore one can say that when ADH is increase water in the tubule is reabsorbed causing a low volume concentrated urine. Decrease ADH will result in a diluted high volume urine.
2. Intercalated cells
- Secretes Hydrogen ions
- Reabsorbs K by a H+,K+-ATPase
For a detailed illustration of their functions, you can check this page here.
Infographic

talkin abt humanaterian assistance dis therminology has to do wt medication its is a great fill in live dat oftain respect and help am a CHEW in ma place am always happy to gv medication i lov and respect meedical line God bless The Doctors, nurses and other division of the field tks
Help me! How do the kidney function when the body is lack of water? And why do we feel thirsty after eating a salty food? Please answer me as soon as possible. Tq
YOU are providing really beneficial knowledge……Keep up this spirit ………tomorrow is A seminar in my biology class and my TOPIC is PCT …….and i know that i will do awesome …….because of this site……
@Siti Hafsah Mohd Afendi
Hi Siti
The answer to Your question is quiet lengthy still I will try to reply it in concise manner
1- When we lack water in our body our kidneys has a system to concentrate our Urine to conserve water for us.
2- This is basically done by Nephrons which are located deep (In Medulla) though they are hardly 25% of all (Rest are in outer area k/as Cortical Nephrons)
3- By the process of active transport a limb of renal tubule (Thick limb of Loop of Henle) sodium & Chloride ions are transported in interstitium of Deep Medulla to make it Hypertonic.
4- This hyperosmolarity at one hand attracts water (Under influence of a hormone ADH & otherwise also) from tubule on other hand concentrates solutes in tubule.
5- Blood flow to this are is very sluggish (Through Vasa Recta) that doesn’t take much ions out of this area but it takes water slowly out ti maintain high Osmotic Conc. in this are to trap more water further.
6- Apart from this the Urea that reaches there (In last part of tubule) is not fully excreted but transported to medullary interstitium to maintain great Conc. there to trap more water.
So because of concentration mechanism & hormone ADH water is absorbed back & stays there.
8- Finally when water is less in our body, the concentration of ions increase in our body & that is sensed by Osmoreceptors of brain (Hypothalamus).
9- It send signals to another gland of brain (Posterior Pituitary) initiating secretion of ADH that works as discussed above (Hypothalamus also synthesize that- Post Pit. just stores & secrete it)
10- On other hand Thirst center that is located i Hypothalamus are also stimulated encouraging us to drink more water.
Joint effect of this (A- Conc. Mechanism +B- ADH Hormone + Stimulation of Thirst Center) results in conservation of water