Immunity
We have often heard the word immunity or resistivity of the body or general weakness of the body. What exactly do people mean when they say these words?
What is Immunity?

According to the modern definition, immunity is described as the ability of the body to recognize, neutralize, or destroy harmful foreign substances in our body. It is the same as the resistivity of the body.
In normal language, immunity can easily be termed as the defense system of our body. Our body needs specific optimal conditions for temperature, pH level, amount of water, food, etc to function properly. Also, a lot of foreign substances like bacteria, microorganisms, dust particles, and such enter our body while we breathe or eat or come in contact with infected materials. When some activity of these foreign substances threaten to disrupt the normal functioning of the body, the active defense factors of our body gets activated.
Types of Immunity
Immunity is classified in two types: Innate Immunity and Acquired immunity.
Innate Immunity
Innate immunity is also called Natural Immunity of the body. It is the inborn ability of the body to protect itself against pathogens and is transferred from mother to the baby. Since it doesn’t depend on previous exposure to microorganisms, it is also known as non-specific immunity. It is always available to protect the living body. The main strategy of innate immunity consists of various barriers that prevent their entry, or they immediately destroy any pathogens that enter our body.
Various Barriers of Natural Immunity
This natural immunity system of our body can be easily compared to an army of a country. Like a country has several defense systems in place e.g.: troops at the borders, troops sent out to war, spies, etc. , similarly our body too has multiple layers or barriers of defending itself from possible foreign invasions. These are:
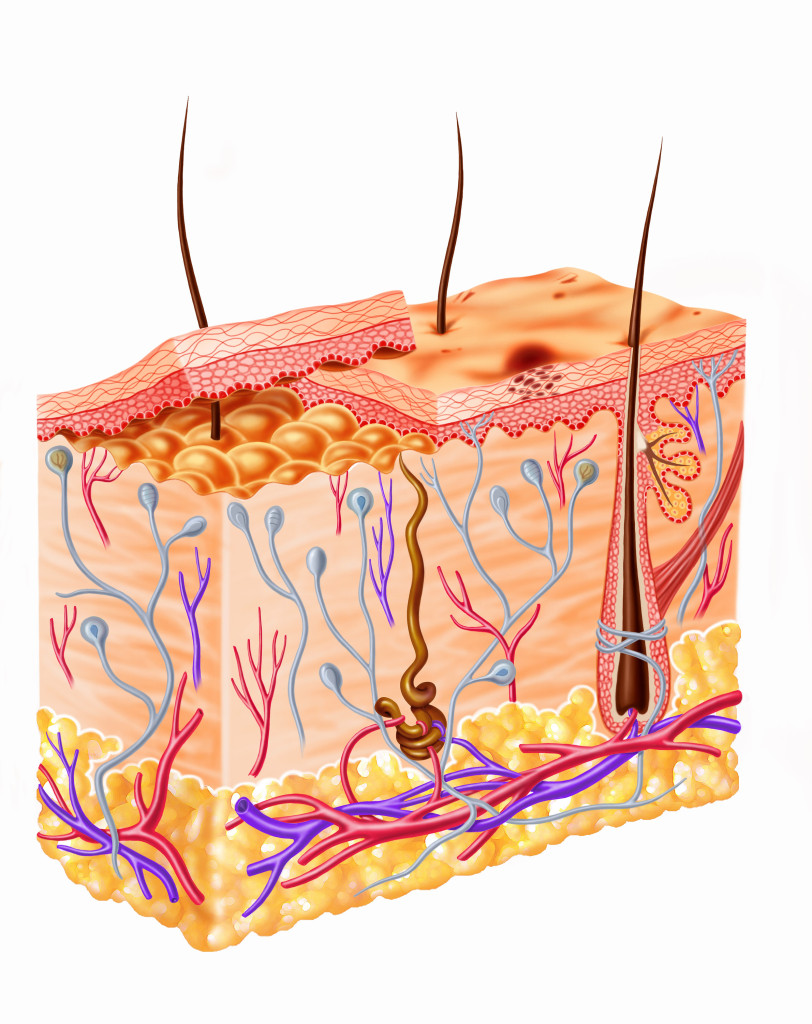
Anatomical barriers
This is the outermost layer of defense. Periodic shredding of epidermis cells and mucous membranes form the anatomical barriers of the body. The microorganisms get trapped in the mucous membranes and are eventually eliminated from the body. Mucous membranes in the nose, as well as ear and skin are all a part of this barrier against germs.
Physiological barriers (exclusive body weather control)
Our body has the unique capability to control its physiological aspects like temperature, pH level and various bodily secretions which acts like a natural fence and sometimes weapons against the harmful substances. Some of these are always present (fence) and some are present in response to an infection (weapons).
One of the examples for the “fences” is acidity of gastric juice ( pH 1.2 to 3.0), which helps in digestion, as well as protection. Our stomach contains concentrated hydrochloric acid (0.5% of gastric juice) strong enough to dissolve any microorganism that comes in contact with it.

Fever is a weapon of the body against an infection. Our body knows that high heat inhibits or stops the growth of various microorganisms. So what does it do?
You’re right. It goes ahead and torches them to retardation and death by raising the temperature of the bodily environment which is also commonly known as fever. It is one of the most common immunological responses of the body.
Another example is diarrhea where the body gathers all the water in your system with excess salts temporarily paralyzing the microorganisms, creating a kind of flood which flushes the harmful substances right out of your body.
Phagocytic barriers (Troops)
Like any well-equipped army, our body too contains soldiers in the form of leucocytes equipped with various enzymes which neutralize or destroy the foreign objects. These are also known as phagocytes. ‘Phago-‘ comes from Greek Phagein which means ‘to ingest’ or ‘devour’. So, these awesome little soldiers go right ahead and actually eat the invading microorganisms. How cool is that?
The three basic types of phagocytes are macrophages (which will eat anything and ‘inform’ the others), neutrophils ( which either eat, poison, or lay traps for pathogens, and help others), and monocytes (which are capable of doing all of the above).
Inflammatory Barriers (special protection)
Inflammatory barriers provide protection to the body while wound healing. Through a wound or an ulcer, microorganisms get direct entry into the human body, and could forgo all the other immunological barriers. Thus, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections.
To prevent the entry of microorganisms, the body stations specialized soldier cells at the site of the wound to attack and destroy any pathogens that may enter through the wound or an ulcer.
Recommended to watch
To get a rough idea of what immunity is, you can watch the video below:
Click Here to Watch Ozzy and Drix
Ozzy is a monocyte and Drix is an antibody. Their main aim is to capture any criminals, i.e. pathogens in the city of (body of) Hector. Since it is sci-fi, some of the facts are pretty distorted, but you get the basic idea and it is extremely fun to watch.
